Logistic regression
Compared to linear regression
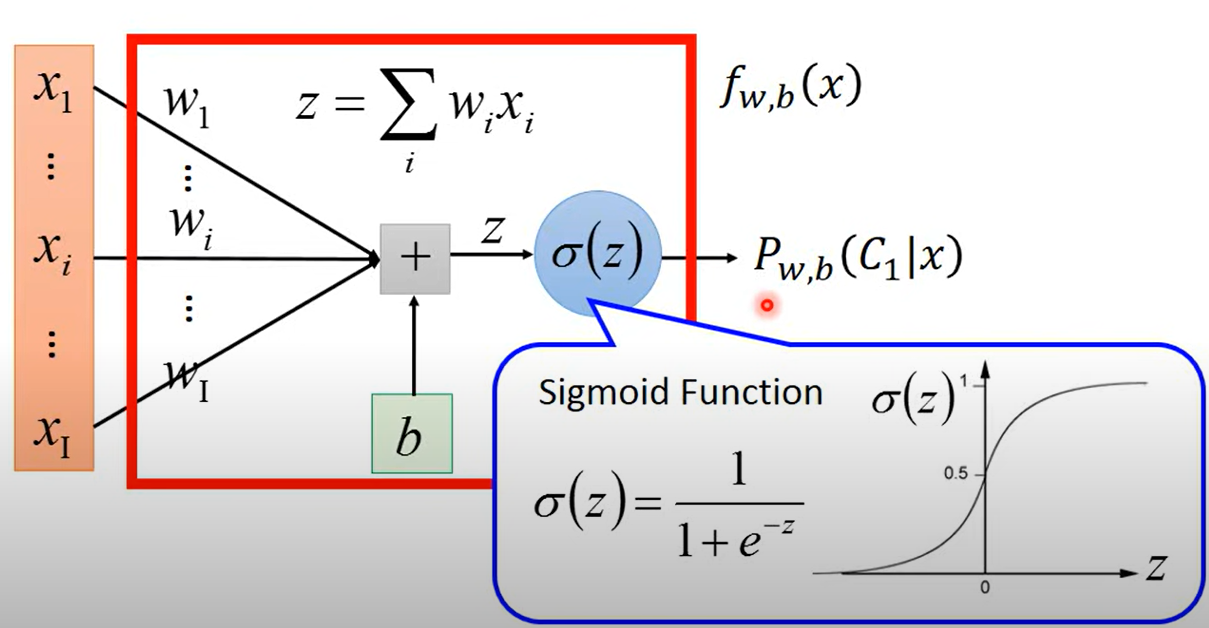
model
- function sets
- 函数定义不同
- logistic 经过了sigmoid,输出一定在0和1之间
- linear 输出什么都行
loss function
-
goodness of a function (Loss)
- 假设训练集是产生的(即函数能描述真实数据集),最大化概率得到最优的
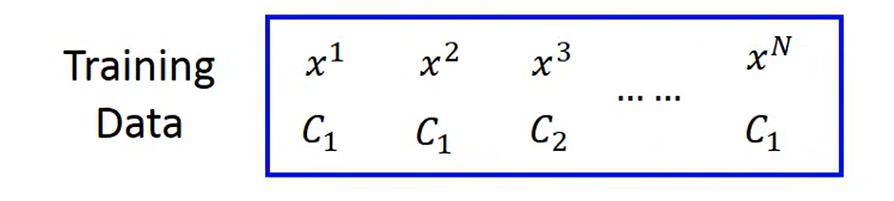
- 最大化概率等价于
- 拆开转化一下
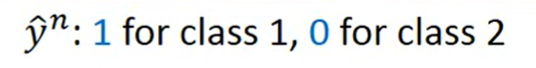
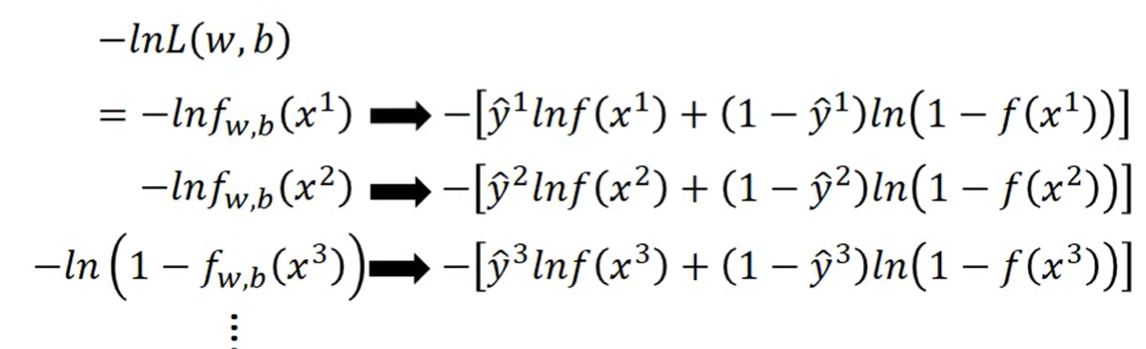
- 就可以得到
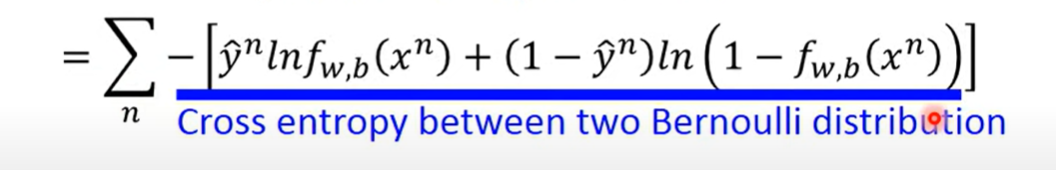
- 这个实际上两个伯努利分布的cross-entropy
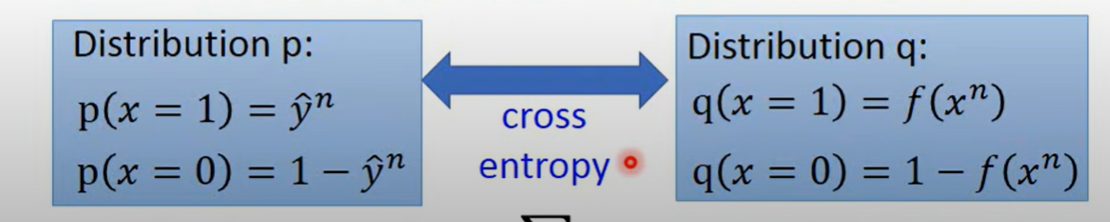
- corss-entropy
- 所以loss是
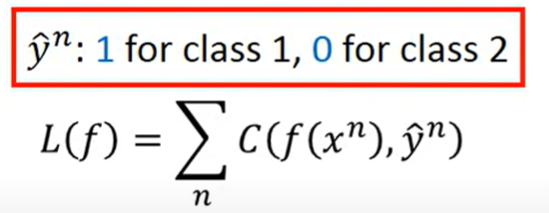
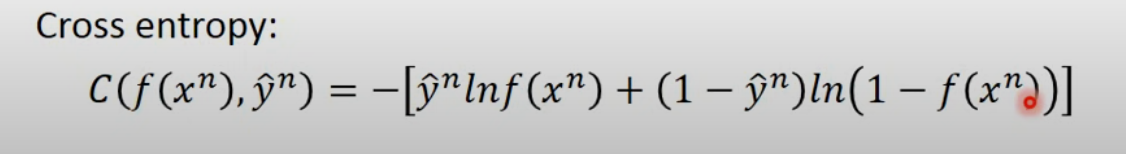
-
Linear
- Square Error
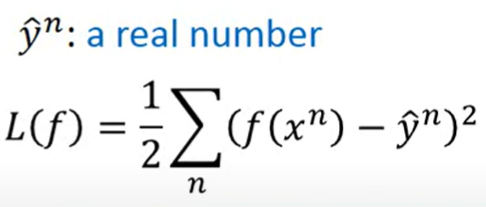
- 两类的话
Training
find the best function
微分
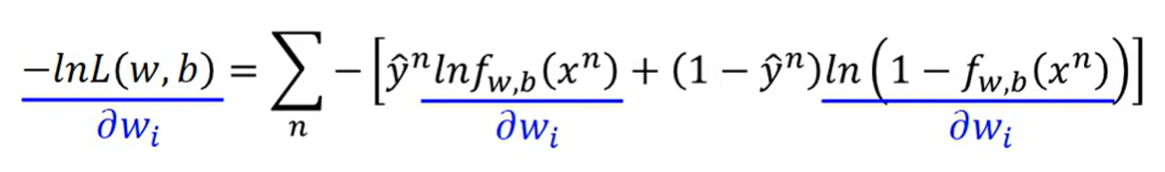
其实是
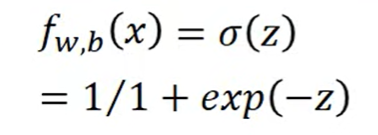
z和w有关
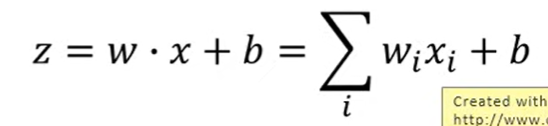
微分得
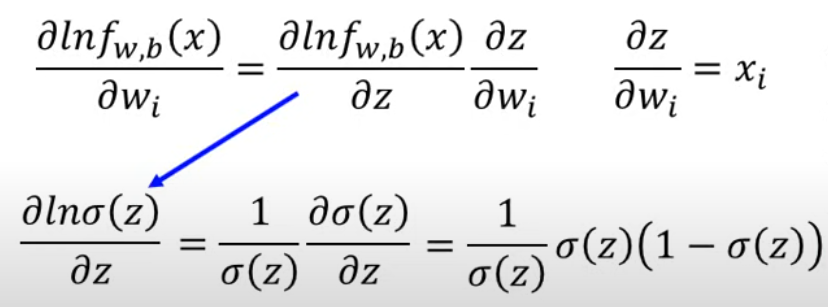
相抵消,同时
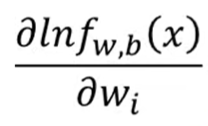
就是
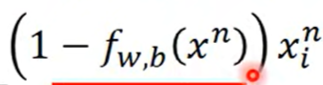
同理对后一项微分得
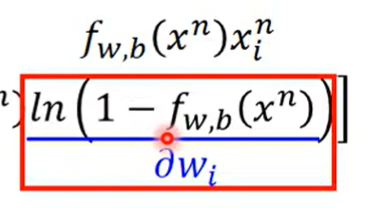
代入展开得
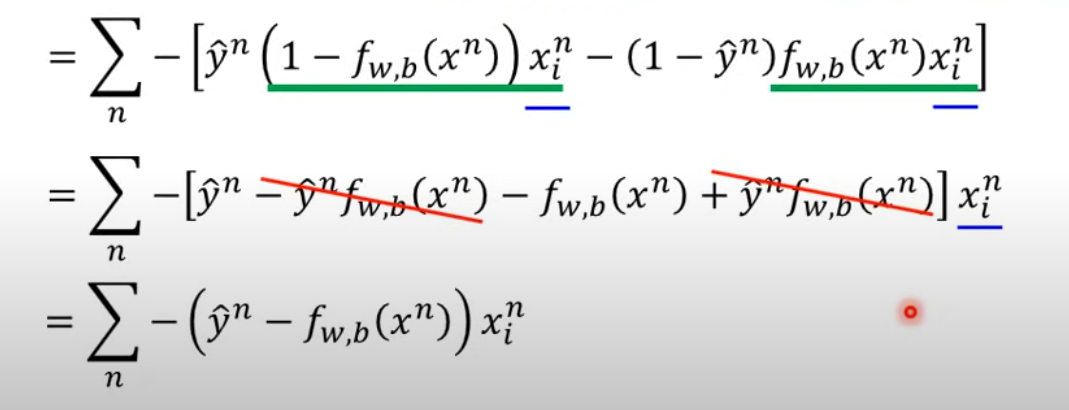
如果是Gradient descent
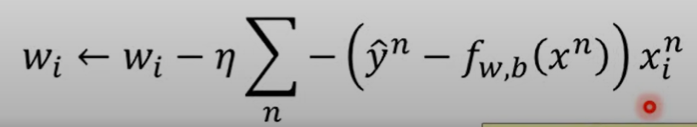
-
结果来看,参数更新取决于三件事
-
学习率
-
训练集
-
结果与实际结果的距离
- 距离越大更新越大
-
Linear regression
- 微分之后更新的式子
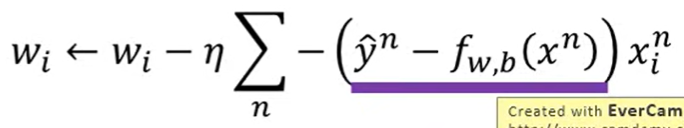
- 一模一样啊一模一样
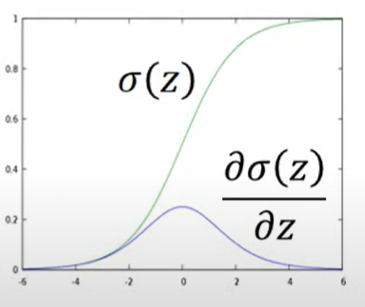
Sigmoid
sigmoid的微分可以直接背起来
Why not Square Error
^c54f03
如果Logistic regression使用Square Error
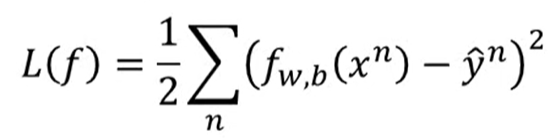
微分得到
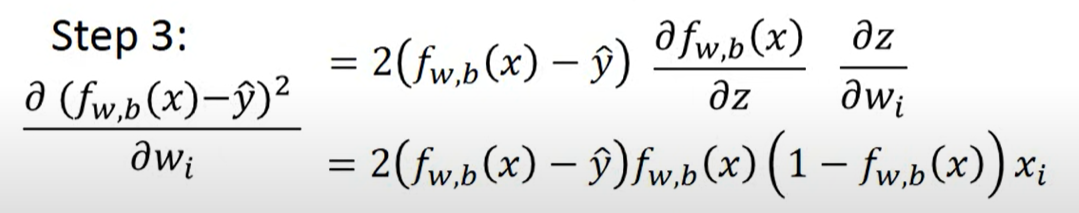
发现

- 当是第一类时,
- 预测结果是第一类,和目标很近,梯度为0,很合理
- 但是如果预测结果是第二类,在另一个极端,和目标很远,梯度也为0

- 当是第二类时,
- 预测结果是第一类,梯度为0
- 预测结果是第二类,梯度也为0
从本身的式子来看,当模型输出十分接近某个类别,梯度就等于0
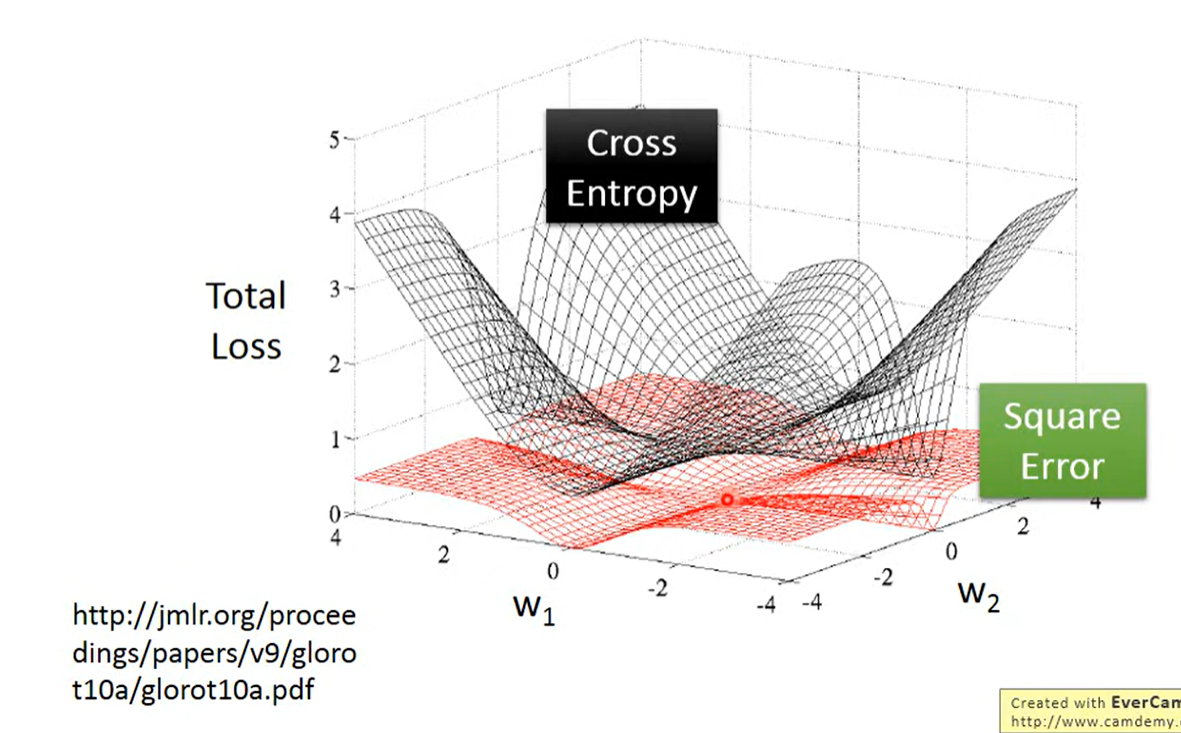
- 黑色cross-entropy,红色square error
- Cross-entropy距离越远(loss越大),梯度越大,坡度越大,很合理
- 但是Square error,loss很大的时候是平坦的
Discriminative v.s. Generative
Logistic regression 称为 discriminative方法
两种方法的初始模型是一样的,但是假设不一样
- generative 假设数据遵循Gaussian distribution(或其他的分布假设)
- discriminative直接找,而Generative找计算出
- discriminative model 表现比较好
虽然Logistic regression可以从generaive方法推导出来,但是logistic regression并没有限制在Gaussian distribution中,推导只是证明二者在结果上等价而已。
Why dicriminative better
Generative的假设限制了模型
给定如图数据集,考虑 属于哪个类别
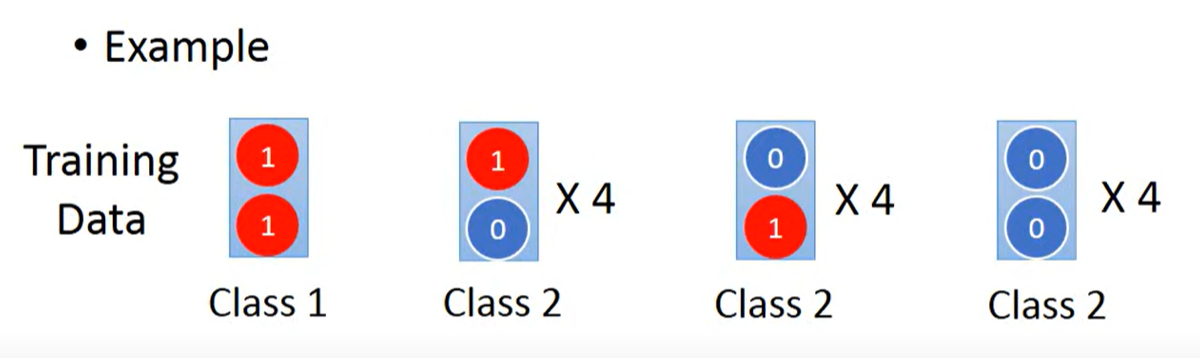
很明显是类别1,但是如果通过Naive Bayes(Generative)计算
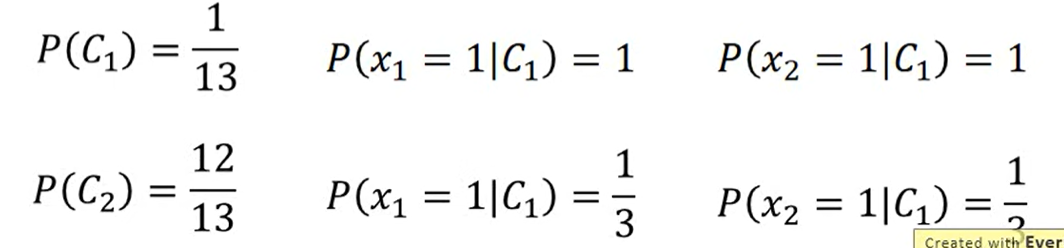
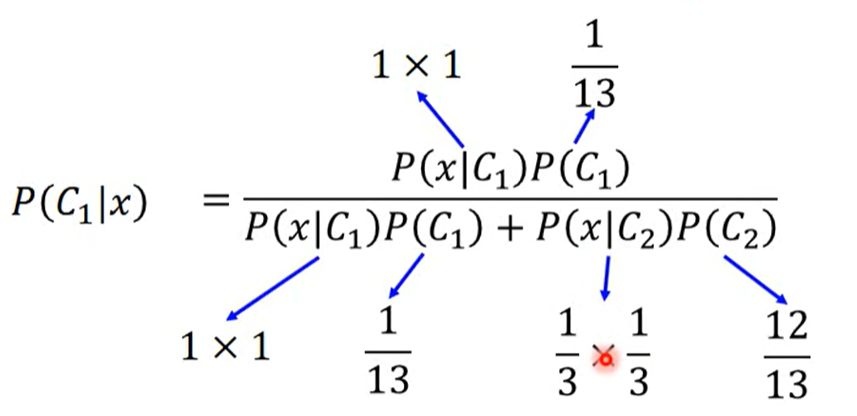
结果小于0.5,所以Naive Bayes认为属于类别2
- 在Naive Bayes中,不考虑特征之间的covariance,认为每个特征是独立sample出来的
- 所以尽管在类别1的数据集中出现过,并不代表属于类别1,只是类别2的数据集中恰好没有sample出而已
However
- 在有假设的情况下,
- 需要的训练集越小
- 对噪声更鲁棒
- 假设后将模型表达式拆开,对从不同来源中学习不同参数有利(Priors and class-dependent probabilities)
Discriminative model受数据量影响更大,有时数据量少时Generative model会比较好
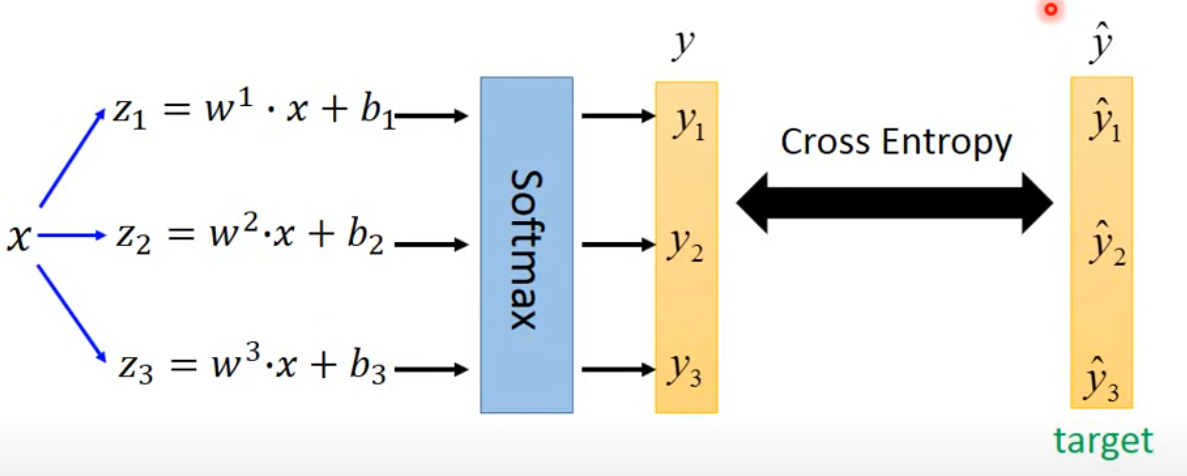
Multi-class classification
3 classes as example
计算
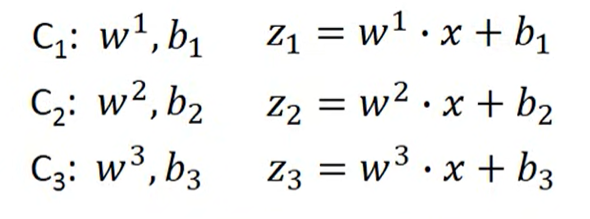
过softmax归一化
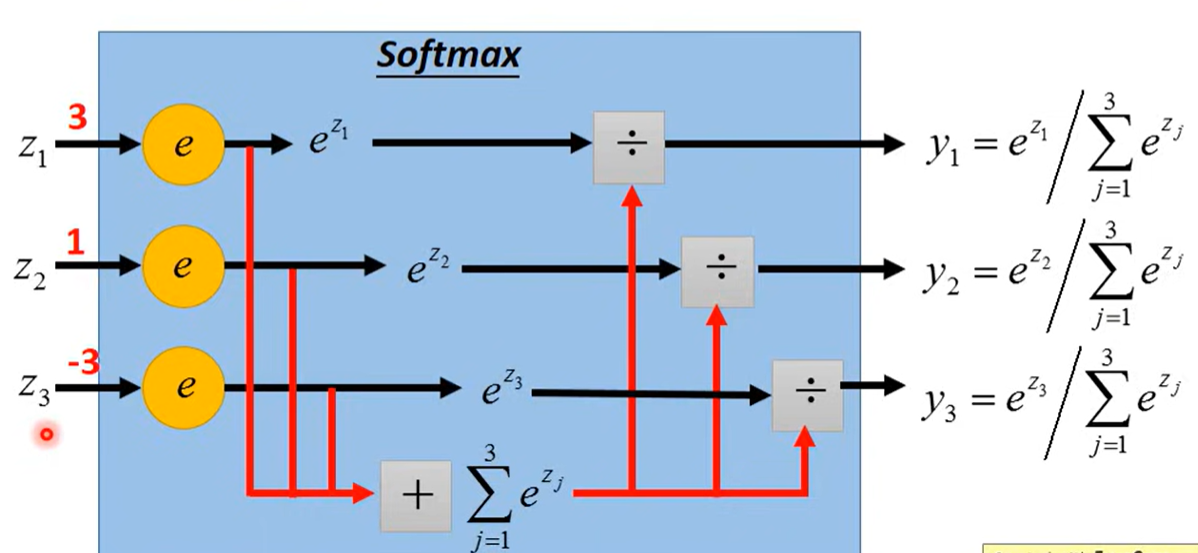
这个推导可以看 《Pattern Recogition and Machine Learning》p0.9-210 或者Maximum Entropy
然后计算cross-entropy
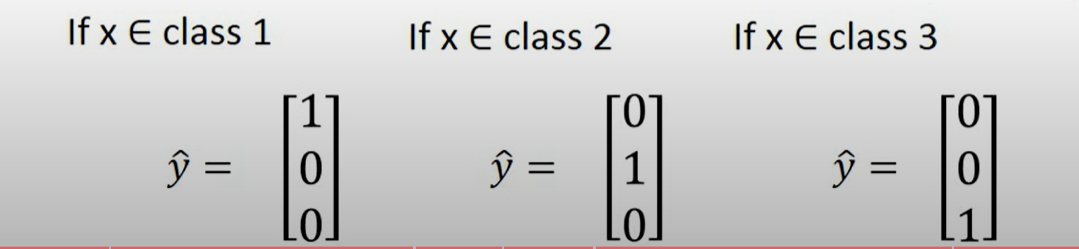
Limitation of Logistic Regression
logistic regression 是线性的函数,两个类别之间的boundary是直线
所以类别之间如果没办法被直线切分的话模型失效
此时可以使用Feature Transformation将特征变成可以被直线分割的情况
但是Feature Transformation很难做到,尝试借助机器学习来实现Feature Transformation
将经过一次logistic regression model的feature,作为一次feature transform的特征
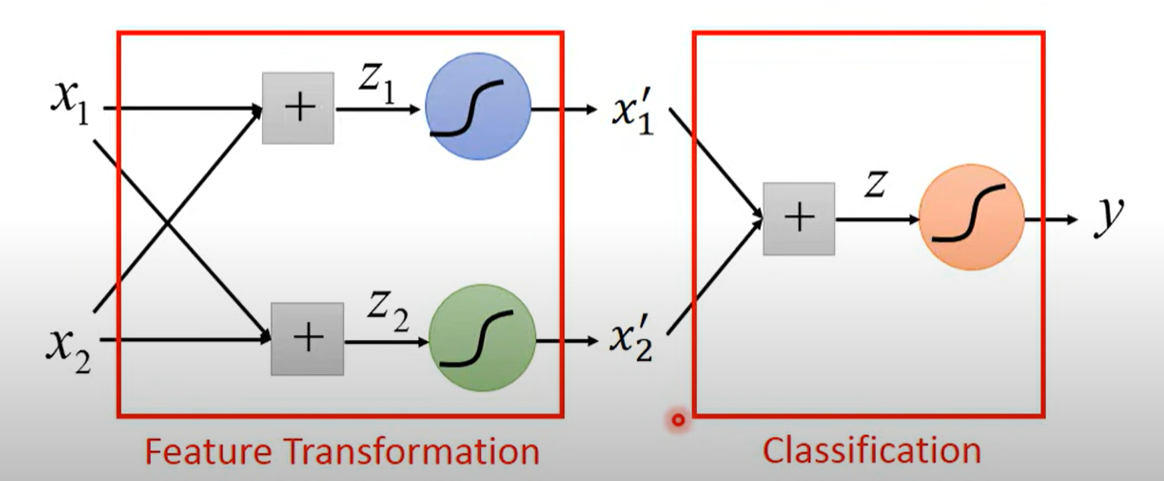
每个logistic regression称为一个neuron,合起来称为Neural Network,也就是deep Learning