Data Augmentation
Data Augmentation is a technique used to artificially increase dataset size.
take a sample from the dataset, modify it, add it to the dataset.
or use DL model to generate data instead(Synthetic data 合成数据).
- helps overcome the “not enough data” issue, prevent overfitting
- do not need to collect data or label data
What’s more, although clean data is neceesary for high-accuracy models, if cleaning reduces the representability of data, then the model cannot provide good predictions for real-world inputs. Data augmentation techniques can enable machine learning models to be more robust by creating variations that the model may see in the real world.
When to use
- prevent models from overfitting
- training set is too small
- improve the accuracy
- reduce operational cost of labeling and cleaning the raw dataset
Audio Data Augmentation
- Noise Injection
- add gaussian or random noise
- Shifting
- shift audio left or right with random seconds
- Changing the speed
- stretches times series by a fixed rate
- Changing the pitch
- randomly change the pitch
Text Data Augmentation
- Word or sentence shuffling
- randomly changing the position of a word or sentence.
- Word replacement
- replace words with synonyms
- Syntax-tree manipulation
- paraphrase the sentence using the same word
- Random word Insertion
- inserts words at random
- Random word deletion
- deletes words at random
Image Augmentation
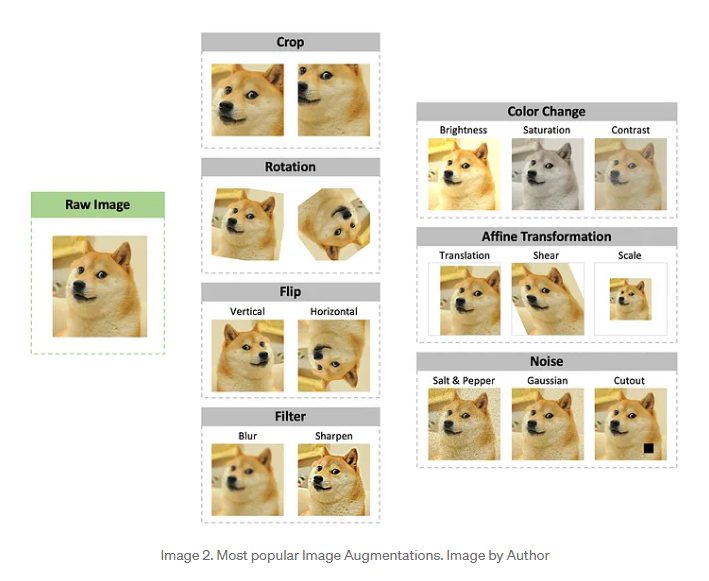
- Geometric transformations
- randomly flip, crop, rotate, stretch, and zoom images. You need to be careful about applying multiple transformations on the same images, as this can reduce model performance.
- Affine Transformation 👈不是很理解是什么
- any transformations that preserve parallel lines
- Kernel filters
- randomly change the sharpness or bulrring of the image
- Adding Noise
- Adding Noise — such as blackening and whitening random pixels (salt & pepper noise), adding Gaussian noise, or even removing the whole region from an image (cutout).
- 加噪声或者移除部分图片
- Color change
- change makes the image darker or brighter, greyscaled or extremely saturated, less or more contrasted.
- Mixing Image
- blending and mixing multiple images
- CutMix and MixUp In Pytorch
- Normalization
To apply augmentation
- Apply a single augmentation or a sequence
- change the order in which augmentations are applied 多种增强,多种顺序
- randomize augmentation parameters, like rotation angle or brightness range 随机参数
- randomize the probability of particular augmentation to be applied 随机概率实施?
Pay attention to the dataset labels. Some augmentation may change labels, like bounding box
How to Choose Augmentations
- Domain expertise
- Business need
- common sense
Domain expertise
depending on the project, some data augmentations make sense, and some just not.
example collected by Complete Guide to Data Augmentation for Computer Vision | by Olga Chernytska | Towards Data Science
- For satellite images, a good choice would be cropping, rotations , refections, and scaling.
- do not introduce distortion to objects like buildings

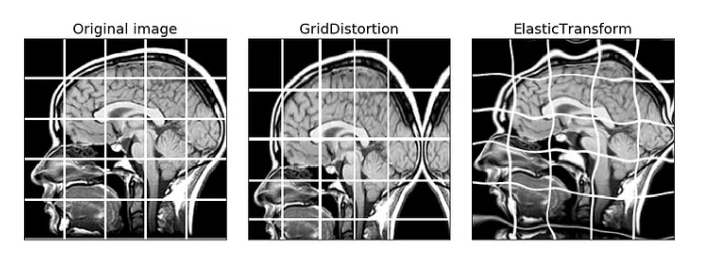
- for medical images, It could be color transformations, grid distortion, and elastic transform
Business need
Does your project need to understand the augmented data?
Common sense
Based on common sense
Or just try it out directly
Limitations
- The biases in the original dataset persist in the augmented data
- quality assurance for data augmentation is expensive