references
Non-linearity
To approximate non-linear functions is the goal of the non-linearity.
sigmoid and Tanh are typical examples of non-linearity
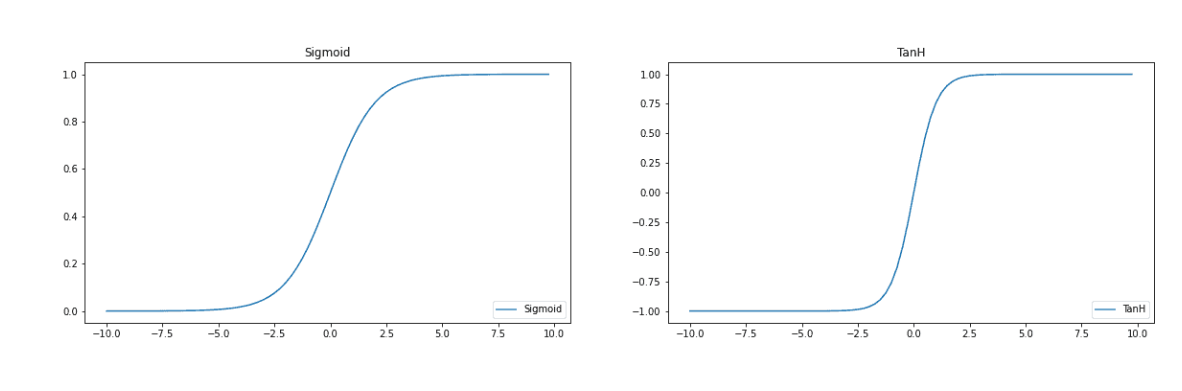
Saturating Non-linearity
A saturating non-linearity is a function that squeezes the input into a fixed(bounded) interval.(将输入挤压到固定边界之间)
sigmoid is a saturating non-linearity
a function is non-saturating if
non-saturating only proposes that the function has to grow to infinity in one direction
The problem
saturating non-linearities will lead to a binary state for a neural network block, if the input close to the boundary.
this reduce the representational capacity of the block.
For a saturated unit, a small change in the incoming weights will have almost no influence on the output of the unit. It will be hard for network to update the weights. As a result, the training algorithm will stagnate(停滞).
when saturate, their gradient will be not very infomative.
饱和状态下,权重的改变对输出造成的影响很小。
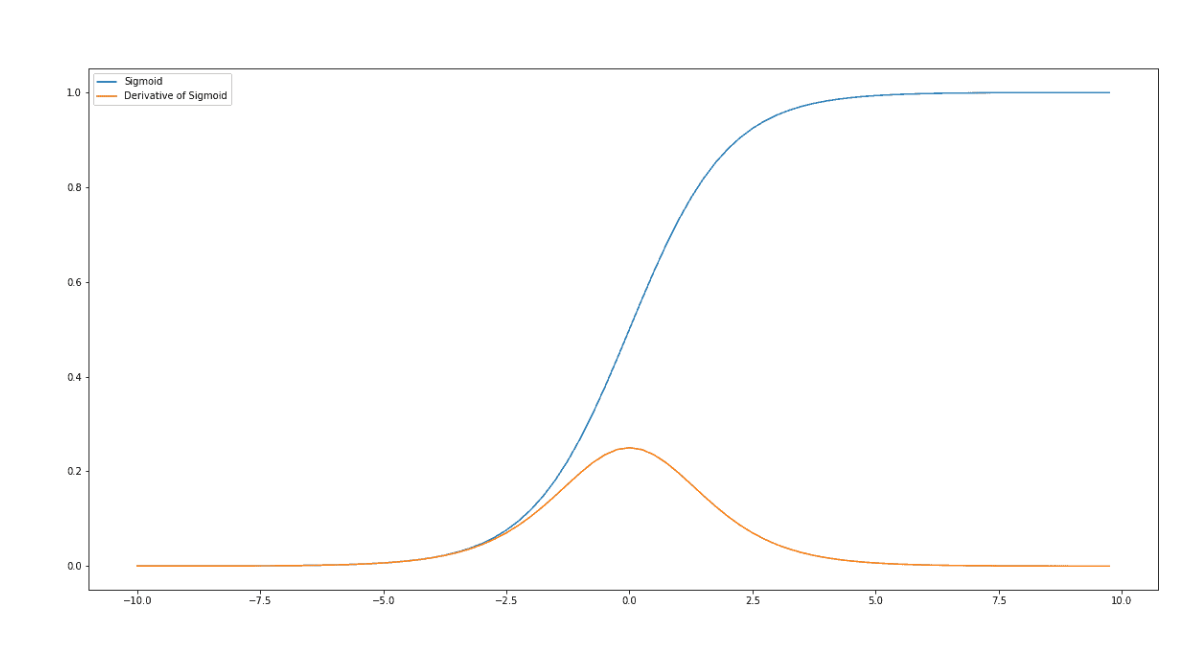
在sigmoid中,尽管输入改变很大,梯度在饱和处变化很小。
if the gradient is small, caused by a saturating non-linearity, then earlier layers will receive only a very limited signal. This problem is known as the vanishing gradients problem.
If we are considering a binary-coded output, then, binary saturating outputs might appear to be appropriate. A downside of saturation is that the outputs don’t indicate a level of confidence. All patterns will be classified with the same or similar strength, even those that are not fit as well. This restricts the model when improving the solution. 尽管可能适用于二元的输出,但是saturating linearity 没有置信度,不管是否完全匹配,会很轻易地得到其中一端
Solution
- non-linearities that don’t saturate. —ReLU
- batch-normalization
- 在输入到激活函数之前进行归一化
- weight initialization
- He initilalization
- residual connections