Overview
almost copy from deep learning
In machine learning, norm is a function that measure the size of vector
The norm is given by
for ,
Intuitively, the norm of a vector measures the distance from the origin to the point
Rigorously, a norm is any function that satisfies the following properties:
- (triangle inequality)
The norm, with , is known as the Euclidean norm(欧几里得范数). It is simply the Euclidean distance.
norm is used frequentily in ML, and often denoted simply as
It is more common to used its squared version, which can be calculated simply by
squared norm is more convenient to work with mathematiocally and computaionally, for example, each derivative of the squared norm only depend on the corresponding element of , while norm depond on the entire vector
In other contexts, the squared norm may be undesirable because it increases slowly near the origin.
It maybe important to discriminate between elements that are exactly zero and elements that are small but nonzero, and thus we turn to norm
norm increase at the same rate(linear) in all location, but retains mathematical simplicity
norm can be used as a substiture for the number of nonzero entries
other norm may needed include max norm norm
It is the maximum absolute value of the components of the vector.
In the context of deep learning, the most common way to measure the size of a matrix is Frobenius norm:
a analogous to norm
by the way, we can use norm to rewrite the dot product
Regularization with Norm
From PRML
3.1.4 Regularized least squares
Error function with regularization term
where is the regularization coefficient that controls the relative importance of the data-dependent error and the regulatization term .
Regularization aim to cotrol over-fitting, so that Considering adding regularizaiton term on the parameters is naturally
We can use norm to describe the amount or other property of parameters.
Squared norm
the here is added for later convenience
the entire penalty become
This particular choice of regularizer is known in the context of machine literature as weight decay(权重衰减), it encourages weight values to decay towards zero(due to the minimize optimal), unless supported by data.
It provides an example of a parameter shrinkage(参数缩减) (in the context of statistic), lead to a closed form of the objective function
A more general regularizer is sometimes used
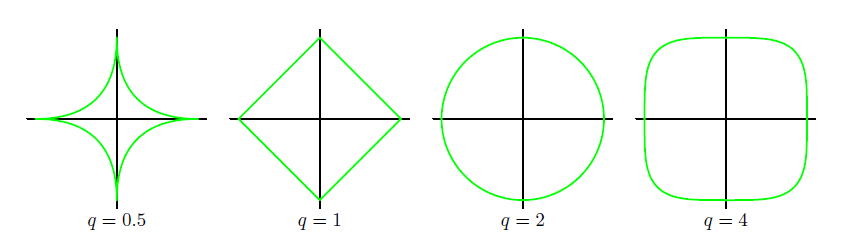
since the norm describe the distance distance from the origin to the point , It can be visulized like
In other perspective, minimizing objetive function with norm( norm or norm) can be calculated using Lagrange multipilers.
in that way, minimize objective function is equivalent ti minimizing the cost function subject to constraint
It can also be visualized like the picture above
norm would lead to a sparse model in which the corresponding basis functions play no role(系数置0,对应的基函数无效)
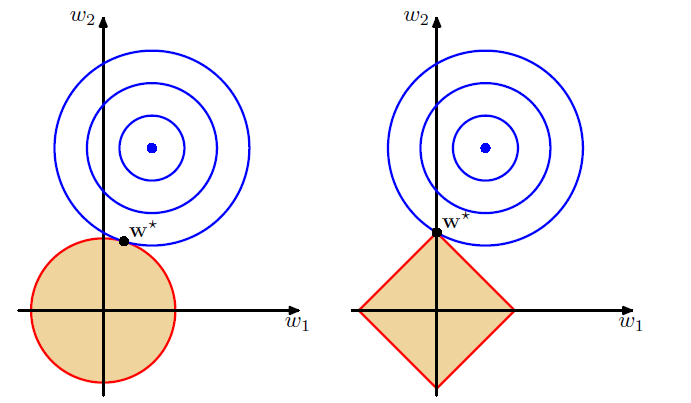
the solution is .
norm in the left and norm in the right
It shows that it (lasso) lead to a sparse solution in which one parameter is 0
It should also be recognized that with regularization, the parameters both decreased